Overview
The Rao lab is focused on understanding the immune dysregulation that drives human autoimmune disease. We use a combination of high-dimensional analyses (RNA-seq, mass cytometry), cellular immunology, and murine models to identify and characterize T cell populations that are expanded in lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and other autoimmune diseases.
Immunophenotyping to identify cellular drivers of autoimmunity in patients
We are using high dimensional cellular profiling to identify specific features of immune dysregulation that define axes of immune dysregulation in patients. We are using these approaches to 1) identify activated immune pathways that distinguish different autoimmune diseases, 2) identify cellular biomarkers that may predict response to biologic therapies, and 3) discover pathologic immune pathways activated in patients with rare or unusual autoimmune diseases.
Relevant papers
- Horisberger A, …, Lederer JA#, Zhang F#, Rao DA#. Blood immunophenotyping identifies distinct kidney histopathology and outcomes in patients with lupus nephritis. bioRxiv. 2024
- Dunlap G*, Wagner A*, Meednu N*, …, McDavid A#, Rao DA#, Anolik JH#. Clonal associations of lymphocyte subsets and functional states revealed by single cell antigen receptor profiling of T and B cells in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Nature Communications (Accepted), 2024.
- Wang R*, Singaraju A*, Marks KE*, …, Bass A#, Donlin L#, Rao DA#. Clonally expanded CD38hi cytotoxic CD8 T cells define the T cell infiltrate in checkpoint inhibitor-associated arthritis. Science Immunology. 2023
- Zhang F*, Jonsson AH*, Nathan A*, Millard N*, …, Wei K#, Rao DA#, Donlin LT#, Anolik JH#, Brenner MB#, Raychaudhuri S#. Deconstruction of rheumatoid arthritis synovium defines inflammatory subtypes. Nature 2023.
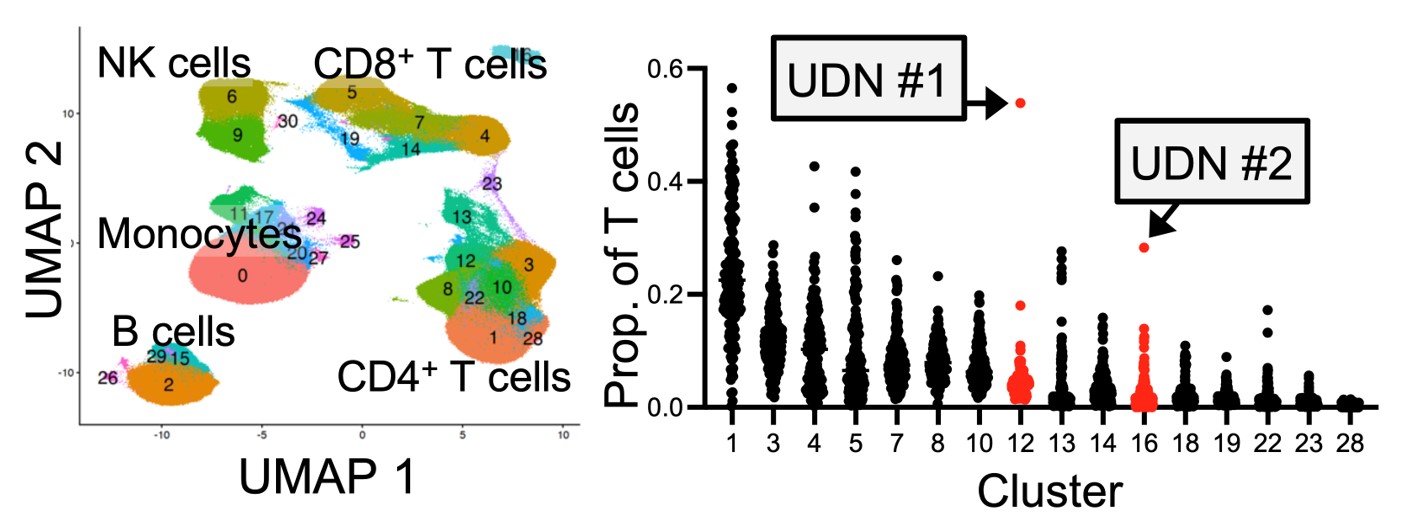
- Mueller AA*, Sasaki T*, …, Rao DA. High-dimensional immunophenotyping reveals immune cell aberrations in patients with undiagnosed inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. J Clin Invest. 2023.
- Sasaki T, …, Rao DA. Longitudinal Immune Cell Profiling in Patients With Early Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022.
- Dunlap GS, …, Kahlenberg JM#, Rao DA#. Single-cell transcriptomics reveals distinct effector profiles of infiltrating T cells in lupus skin and kidney. JCI Insight. 2022.
- Tedeschi SK, …, Rao DA#, Solomon DH#. Rheumatoid arthritis disease activity assessed by patient-reported outcomes and flow cytometry before and after an additional dose of COVID-19 vaccine. Annals of Rheumatic Disease. 2022.
- Zhang F*, Wei K*, Slowikowski K*, Fonseka CY*, Rao DA*, …, Donlin LT#, Anolik JH#, Brenner MB#, Raychaudhuri S#. Defining Inflammatory Cell States in Rheumatoid Arthritis Joint Synovial Tissues by Integrating Single-cell Transcriptomics and Mass Cytometry. Nature Immunology 2019.
Regulation and function of T peripheral helper (Tph) cells
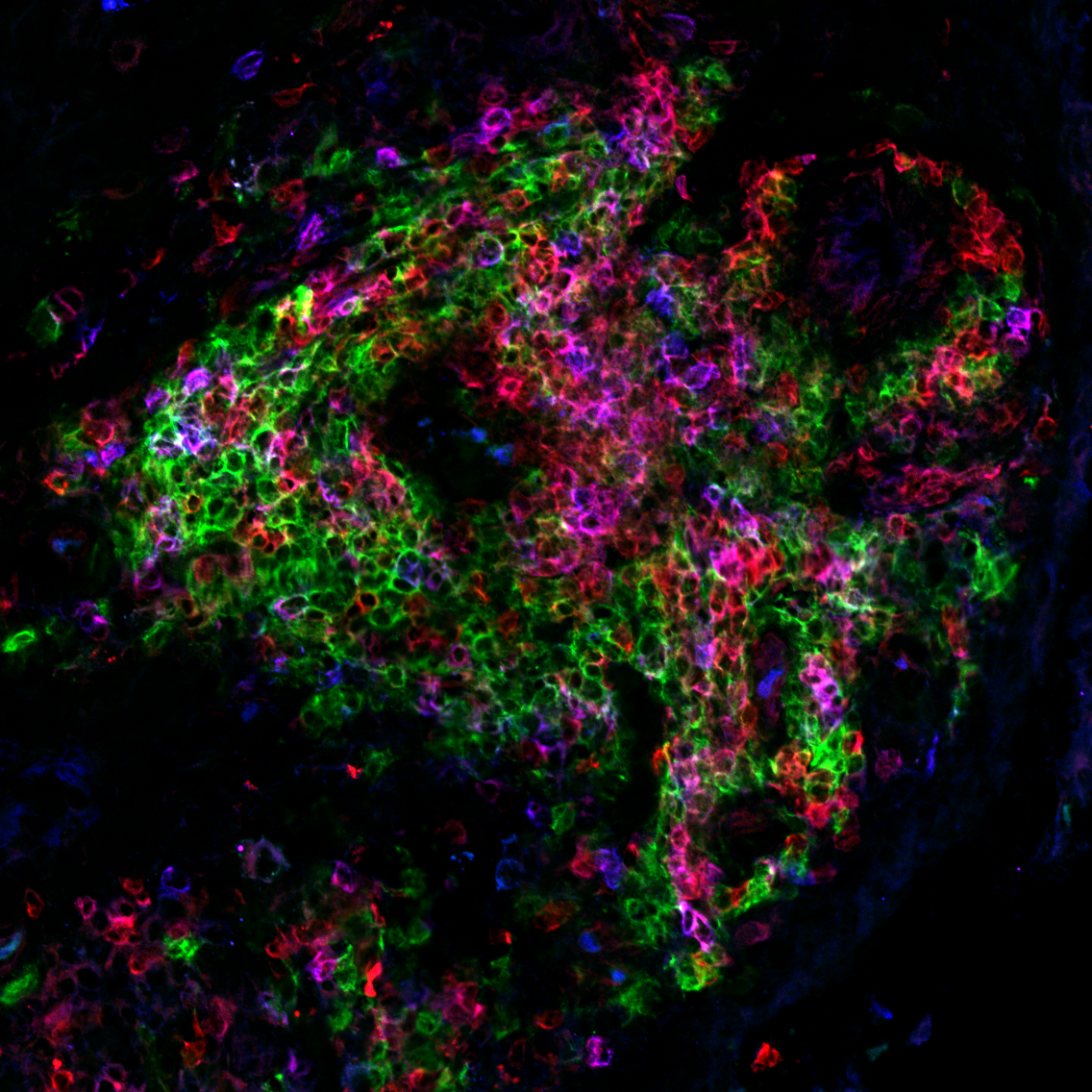
T peripheral helper (Tph) cells infiltrate inflamed tissues, such as joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and drive B cell responses through production of IL-21 and the B cell chemoattractant CXCL13. Tph cells functionally resemble Tfh cells in their ability to stimulate a B cell response, yet Tph cells express a distinct set of migratory receptors that enable their migration to inflamed tissues. These cells are expanded in many autoantibody-associated diseases. Using CRISPR/Cas9 screens, in vitro functional studies, and murine models, we are studying the signals that control both the B cell helper function and migratory capacity of these autoimmunity-associated T cells.
Relevant papers
- Law C*, Wacleche VS*, Cao Y*, …, Choi J#, Rao DA#. Interferon subverts an AHR-JUN axis to promote CXCL13+ T cells in lupus. Nature, In Press. 2024.
- Kim T, Martinez-Bonet M, Wang Q, Hackert N, Sparks JA, Baglaenko Y, Koh B, Darbousset R, Laza-Briviesca R, Chen X, Costa Aguira V, Westra HJ, Gurierrez-Arcelus M, Weirauch M, Raychaudhuri S, Rao DA, Nigrovic PA. Non-coding autoimmune risk variant accelerates T peripheral helper cell development via ICOS. Nature Communications. 2024.
- Bocharnikov AV, …, Rao DA. PD-1hi CXCR5– T peripheral helper cells promote B cell responses in lupus via MAF and IL-21. JCI Insight. 2019
- Rao DA, …, Brenner MB. Pathologically expanded peripheral T helper cell subset drives B cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2017.